Microwave & mmWave Links
Powertec leverage our advanced ‘digital-twin’ terrain and RF analysis toolsets to provide microwave link design services to our clients.
We process detailed 3D models of sites captured from drone photogrammetry and LiDAR scans to develop advanced microwave link feasibility studies. Our team works with leading microwave technology brands and manufacturers to bring together designs that meet even the most demanding data rate / throughput and uptime requirements.
- Five-Nines uptime (99.999%)
- Multi-gigabit and low latency links
- 1+1, 2+0 redundancy and hot-standby builds
- Water reflection mitigation
- Thermal, environmental, and climatic fade analyses
By partnering with ACMA licenced carriage service providers and our national network of installation companies, our team can help bring your network to life.
What is Microwave Communication?
Microwave communication is most common in the form of point-to-point data links, which provide a cost-effective alternative to conventional fibre optic lines. In its most popular usage, data communication is achieved using two highly directional (high gain) antennas which focus a thin beam of electromagnetic waves each other through the open air. This thin beam consists of a channel of closely spaced frequencies which are digitally modulated to carry data. Each microwave antenna is connected to a radio unit which has the task of modulating and demodulating the carrier frequency, that is, sending and receiving the data.

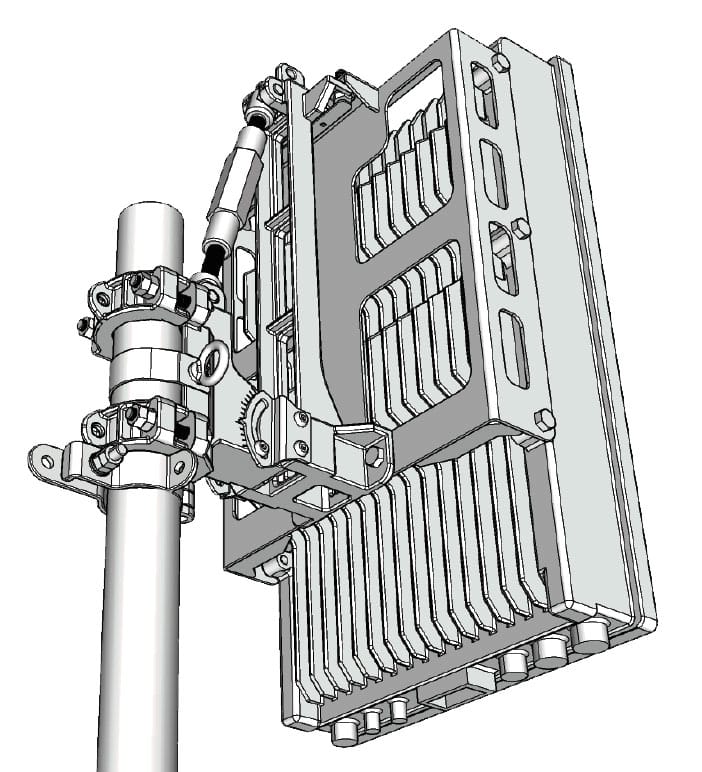
Fundamentally, this is all microwave communication is. In practice however, microwave communication can be extremely complex. Unlike fixed line communication like fibre optics, microwave uses an unprotected transmission medium affected by the environment. Factors that may affect a microwave link include:
- Free Space Path Loss (FSPL)
- Rain / humidity / precipitation
- Ambient temperature
- Air refraction (k-factor)
- High wind (wind load)
- Hostile microwave links
- Solar radiation
- Pollen count
- Vegetation growth
- Terrain reflections
- Equipment ageing
- Vandalism
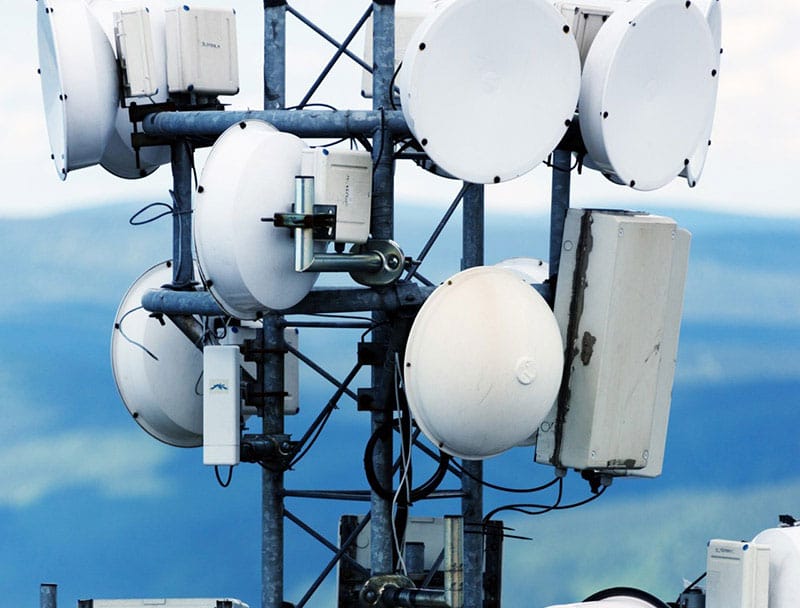
The Latest Microwave & mmWave Technologies
Today, modern microwave radios are almost exclusively in an all-ODU format, connected into wider telecommunications networks using SPF fibre optic cables. Data rates as high as 10 Gbps are achievable using 8KQAM / 8192QAM modulation schemes. With many conventional microwave bands (such as 26, 28, 39 GHz) refarmed for 5G, E-band (70 / 80 GHz) microwave has become a popular choice for high capacity, short range backhaul.
With most countries implementing fibre-optic based national broadband infrastructure, the use of microwave as a primary data connection is falling out of favour. The technology however has become popular as a failover service and remains critical for last-mile communications. Low-cost microwave radios, such as those developed by Cambium have become a ubiquitous part of the landscape in developing nations, and regions where national broadband infrastructure has yet to reach.


Let’s Connect
Critical connectivity demands the support of a telecommunications partner who has stood the test of time.
Contact our team today to discuss your microwave network requirements.
Request a Free Consultation